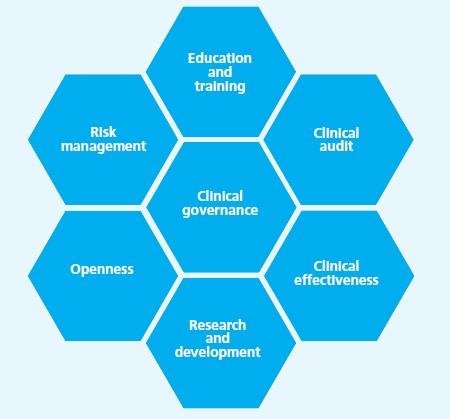
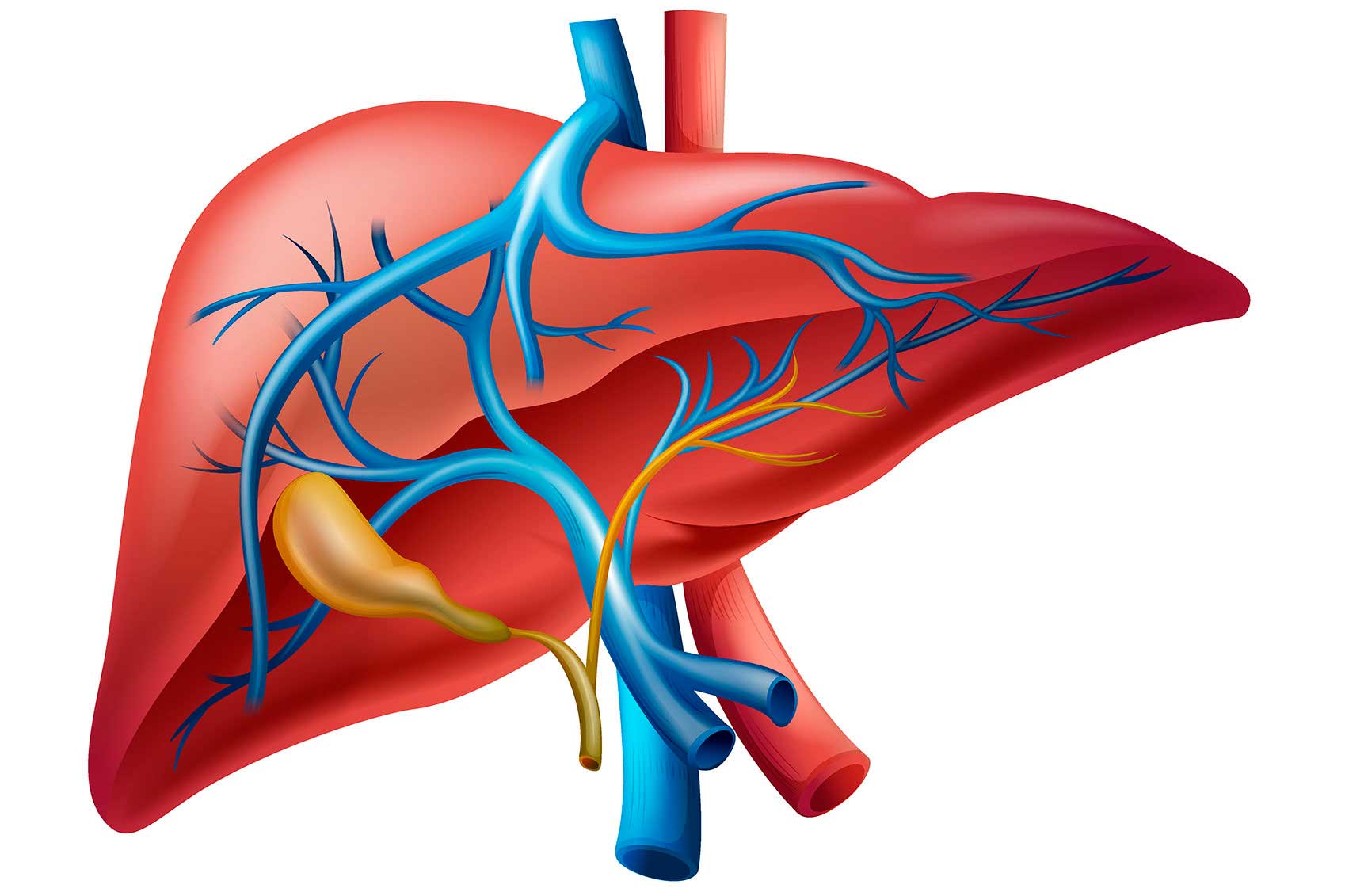
Emergency medicine is a vital field of medical practice that focuses on the prompt and effective care of patients facing acute illnesses or traumatic injuries that require immediate attention. Emergency medicine specialists, known as emergency physicians, are trained to assess and manage a wide range of medical conditions, from heart attacks and strokes to severe accidents and critical infections. They work in fast-paced environments, typically in hospital emergency departments, where rapid decision-making, excellent communication, and the ability to handle high-pressure situations are essential.
The role of emergency medicine extends beyond diagnosis and treatment. Emergency physicians must stabilize patients, initiate life-saving interventions, and coordinate with other medical specialists to ensure the best possible outcome. They play a critical role in triaging patients based on the severity of their conditions, prioritizing care for those in the most critical condition. Additionally, emergency medicine practitioners often engage in preventive education, teaching communities about safety measures to minimize accidents and injuries that might lead to emergency situations. This specialty is demanding, challenging, and rewarding, as emergency physicians make a significant impact on patients' lives during their most vulnerable moments.



















 s.
s.